Available Technologies
Mathematical Method for Robust Pathological Tissue Image Analysis Without AI
New imaging diagnostic method that enables quantitative comparison and evaluation that compensates for differences in pathologists’ experience
Background
In recent years, the use of AI for diagnosing pathological stained images and classifying cases has become mainstream. However, AI-based image diagnosis relies on staining intensity and color tone as information, making standardization difficult and failing to provide robust metrics for quantitative tissue comparison. Additionally, AI is unreliable in diagnostics since it cannot clearly justify its reasoning thus it is hard to validate against expert pathologists.
Description and Advantages
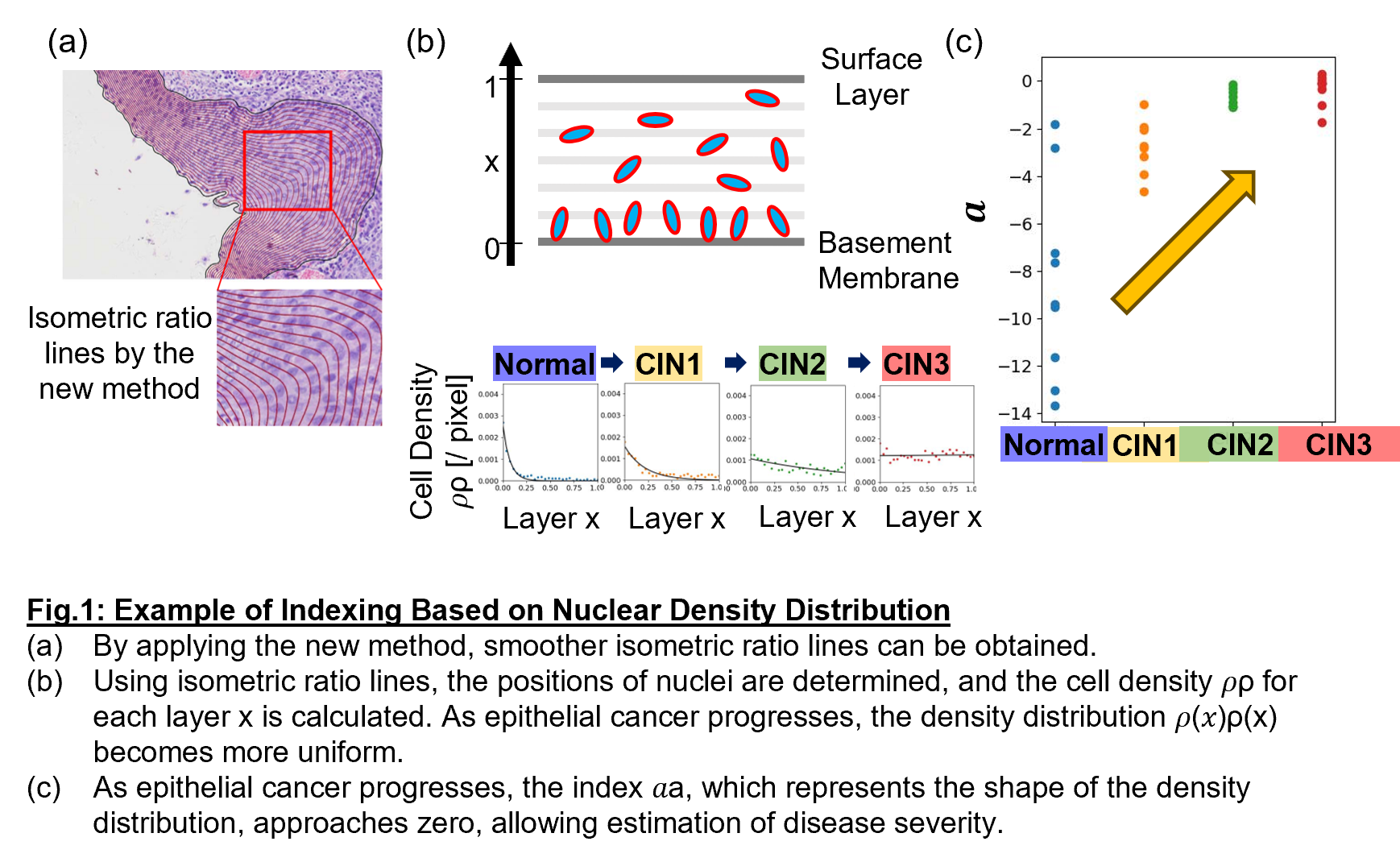
Kyoto University researchers have established a method to quantitatively compare and evaluate pathological images by standardizing cellular information within tissues from multiple perspectives using mathematical approaches. The method enables consistent evaluation even for complex and distorted tissue sections. Furthermore, statistical values derived from multiple quantitative indicators have revealed characteristics corresponding to the progression of epithelial cancer (Fig.1). As a result, disease progression can be numerically represented from histopathological images.
‣Standardization of Pathological Image Diagnosis
By complementing pathologists' experience-based diagnoses with numerical indicators, this method contributes to the standardization of pathological image diagnosis.
‣Output from Mathematical Approaches
The method avoids the black-boxing of decision criteria associated with DL-based AI, providing
reliable and transparent diagnostic results for both patients and medical professionals.
‣Development of Various Software Applications
| Development Status |
Successfully identified core numerical indicators |
|---|---|
| Offer | • Patent License • Option for Patent License |
| Related Links | View PDFView in Japanese |
Have you found what you were looking for?
- Interested in a particular research activity
- Cannot find the information
- Have questions on how to utilize research results
Feel free to contact us and get answers to your questions.
Inquiry- TLO-KYOTO
- Available Technologies
- Mathematical Method for Robust Pathological Tissue Image Analysis Without AI
3rd Floor, International Science
Innovation Building, Kyoto University
Yoshidahonmachi, Sakyo-ku, Kyoto
606-8501 JAPAN


