Available Technologies
Ex-vivo Liver Model Displaying 3D Hepatic Lobule Structure
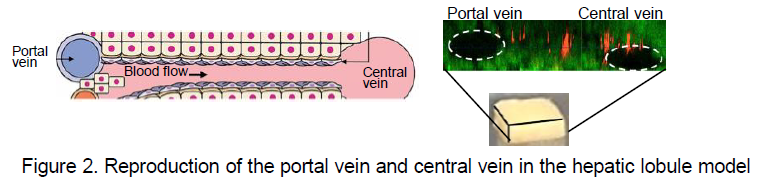
This model replicates the 3D structure of hepatic lobules, incorporating not only hepatocytes and capillaries, but also pseudo-arteries and pseudo-veins.
Background
As the prevalence of liver diseases continues to rise globally, the development of therapeutic drugs has become increasingly important. However, existing animal models face issues such as interspecies differences and ethical concerns, creating a demand for alternative liver model technologies. The human liver is composed of approximately 500,000 hepatic lobules which serve as its structural units. As a result of this highly sophisticated architecture, it is extremely difficult to create three-dimensional liver models that closely resemble the human liver. Moreover, two-dimensional culture systems are associated with rapid functional decline of the cultured cells. Therefore, conventional alternatives to animal models have thus far been unable to simultaneously replicate the hepatic lobule architecture, maintain liver function, and support long-term culture.
Description and Advantages
Kyoto University researchers have successfully developed a model that reproduces the structure of hepatic lobules, including key features such as the portal vein, central vein, and even sinusoid-like architecture. The model also accurately reflects the size of hepatic lobules as found in vivo. By enabling enhanced precision in the spatiotemporal analysis of disease progression and drug efficacy in the liver, this model is expected to serve as a promising alternative to conventional animal studies.
⮚ Demonstration of hepatic lobule structure and function
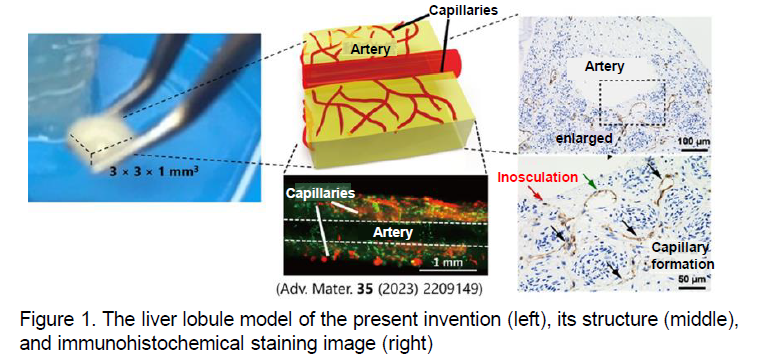
⮚ Ability to replicate liver tissue fibrosis induced by carbon tetrachloride
Desired Collaborations
⮚ Biopharma companies・CROs・Research Institutions
∙ Drug screening, efficacy evaluation, toxicity assessment, etc.
⮚ Contract Research Partnerships
⮚ Collaborative Fundamental Research
∙ Liver lobule zonation, perfusion systems, etc.
| Development Status |
This hepatic lobule model has been constructed and successfully demonstrated its ability to replicate tissue fibrosis induced by carbon tetrachloride. |
|---|---|
| Publication | Presented at TLO-KYOTO Innovation Matching Seminar YouTube Link (Japanese):https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lpEI-sm4WG8 |
| Offer | ・ Patent license* ・ Collaborative research *Patent application filed by Kyoto University, currently pending |
| Related Links | View PDFView in Japanese |
Have you found what you were looking for?
- Interested in a particular research activity
- Cannot find the information
- Have questions on how to utilize research results
Feel free to contact us and get answers to your questions.
Inquiry- TLO-KYOTO
- Available Technologies
- Ex-vivo Liver Model Displaying 3D Hepatic Lobule Structure
3rd Floor, International Science
Innovation Building, Kyoto University
Yoshidahonmachi, Sakyo-ku, Kyoto
606-8501 JAPAN


